This page relates to inpatient procedures at Huntington Hospital.
To learn more about outpatient imaging, please visit our Imaging & Radiology page.
Imaging & Radiology Technology
Huntington Hospital provides high-quality diagnostic imaging using highly advanced imaging technologies.
If you have any questions or need further information, please call (626) 397-5139.
X-Ray
An X-ray is a painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Radiography involves exposing a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body.
CT Scanning
A computerized tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images to create cross-sectional images (or image “slices”) of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body. Because these images provide more detailed information than is available via X-ray, CT may be recommended in some circumstances. While CT scans have multiple uses, they are particularly helpful in screening for and diagnosing internal injuries (such as those sustained in a car accident) or other types of trauma.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine images body function rather than anatomy. This is done with the use of small amounts of radioactive materials called tracers, each of which is designed for uptake by specific organs or types of body tissue. The tracers are injected into a vein in the arm, inhaled or swallowed. A special camera maps the distribution of the radioactive tracer to create images which are studied by radiologists. Nuclear medicine exams are among the safest available in diagnostic imaging.
What Does the Equipment Look Like?
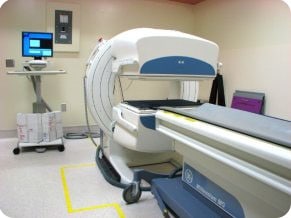
MRI/ Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI does not use ionizing radiation, as CT scans and x-rays do. Instead, MRI generates images using a very strong magnet and radio waves. The images are cross sections like CT scans, but MRI can also produce images in lengthwise planes without the patient having to change position. Not everyone may be a candidate for MRI. Due to the strong magnet used, some implanted materials and devices are not safe to image.
Conventional MRI machines have a donut shape with a tube that is usually about 4-5 feet in length. This exam causes anxiety for some people who are claustrophobic. If you know you are claustrophobic, please let our staff know at the time of scheduling.
Angiography & Interventional Procedures
Interventional radiology is a sub-specialty of radiology that is both diagnostic and therapeutic. Procedures are performed to diagnose and treat medical conditions. Areas of the body are accessed through minimally invasive techniques using imaging guidance.
These radiology procedures often provide alternatives to surgery and have many advantages. They have significantly shorter recovery periods, less severe side effects, less scarring, are often faster and usually don’t require general anesthesia. Many times they can provide options for people who have inoperable conditions or otherwise aren’t candidates for surgery.
What Does the Equipment Look Like?
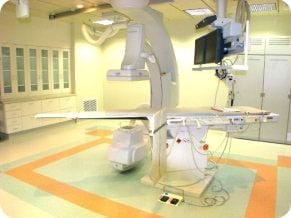
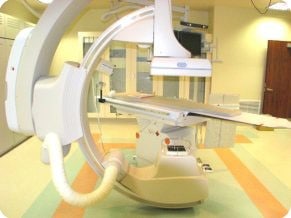
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging (also called a sonograph or sonography) is an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. Sound waves are directed at a particular area of the body and the different body tissues reflect the waves back in varying degrees. The echoed waves are recorded and displayed as a continuous real-time image on a computer monitor. Since the images are real-time, ultrasound has the benefit of allowing the Radiologist to see organs in motion, such as the movement of heart valves and blood flow.
What Does the Equipment Look Like?

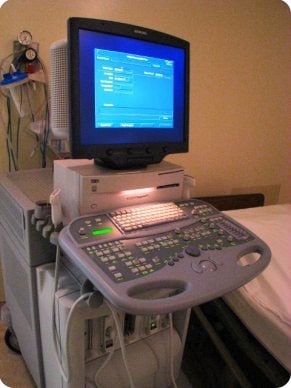
This imaging technique is becoming increasingly important in the diagnosis of a variety of medical conditions in many different organs. Included are:
- View the uterus and ovaries of a pregnant woman and assess the health of her fetus
- Evaluate a breast lump
- Diagnose certain cancers
- Guide a needle for biopsy or tumor treatment
- Evaluate flow in blood vessels
- Diagnose gallbladder disease
- Check a thyroid gland
- Reveal genital and prostate abnormalities
 English
English Espanol
Espanol 简体中文
简体中文 Tagalog
Tagalog հայերեն
հայերեն 한국인
한국인 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt فارسی
فارسی русский
русский 日本
日本 عربي
عربي