A stroke – or brain attack – is a type of cerebrovascular disease that affects the body’s ability to carry blood to the brain. Learn more about stroke below.
Stroke is a medical emergency. It is the leading cause of adult disability and a leading cause of death in the United States.
Time is crucial! Prompt treatment of a stroke could mean the difference between life and death. Early treatment can also minimize damage to your brain and future disability. Time lost is brain lost, so getting a patient to the hospital is critical when seconds and minutes count.
This page includes information about stroke signs and symptoms, the different kinds of stroke, and the risk factors for stroke.
Stroke Signs & Symptoms

Other stroke symptoms may include:
- Sudden blurred, double or decreased vision
- Difficulty swallowing
- Confusion, or problems with memory, spatial orientation or perception
- Seizures, fainting or blacking out
- A sudden, severe headache or an unusual headache, which may include vomiting or altered consciousness
If you see these signs, you should call 9-1-1 immediately.
Types of Stroke
In order to function, the brain needs a constant flow of blood which travels through your arteries (also known as blood vessels). If the blood flow is blocked and the brain cannot get the level of oxygen-rich blood it needs, then the deprived area of the brain begins to die.
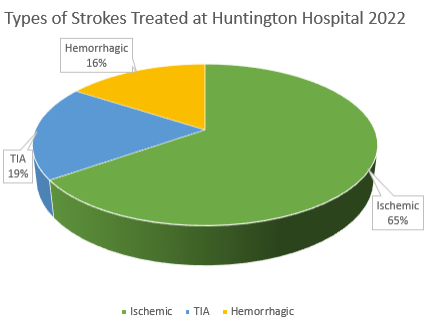
Ischemic Stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when an artery in the brain is blocked. The most common cause is narrowing of the arteries due to atherosclerosis (gradual cholesterol deposits). When the arteries are narrowed, blood cells accumulate and form blood clots (thrombosis). Another cause of stroke is a blood clot in the heart (embolism) from irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation), heart attack or abnormal heart valves.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
An intracerebral hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding within the brain tissue. It is most often caused by high blood pressure which stresses the artery walls causing it to burst and bleed to the surrounding brain tissue.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs in the area between the brain and the thin tissue layer that surrounds it. This is usually caused by an aneurysm, which is a weak or thin spot on a blood vessel wall. Some aneurysms are present at birth and others develop over a number of years and are usually not detected until they burst.
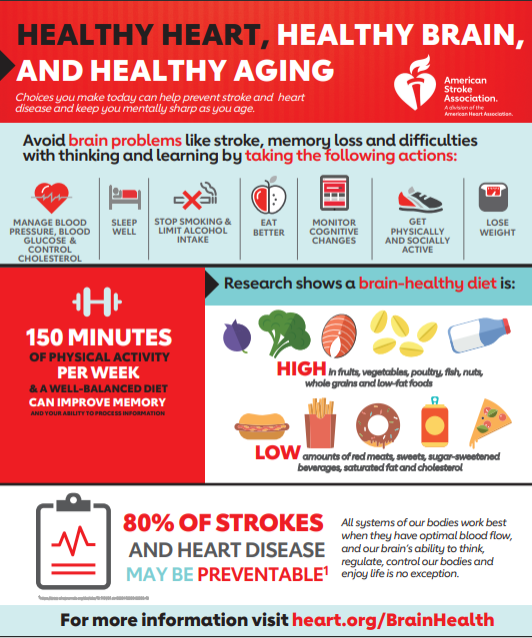
Risk Factors for Stroke
Learn more about risk factors for stroke and what you can do to prevent stroke at Stroke.org.
 English
English Espanol
Espanol 简体中文
简体中文 Tagalog
Tagalog հայերեն
հայերեն 한국인
한국인 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt فارسی
فارسی русский
русский 日本
日本 عربي
عربي